
What a Calcium Score Can Tell You About Your Heart Health
Last Updated
Feb 20, 2026
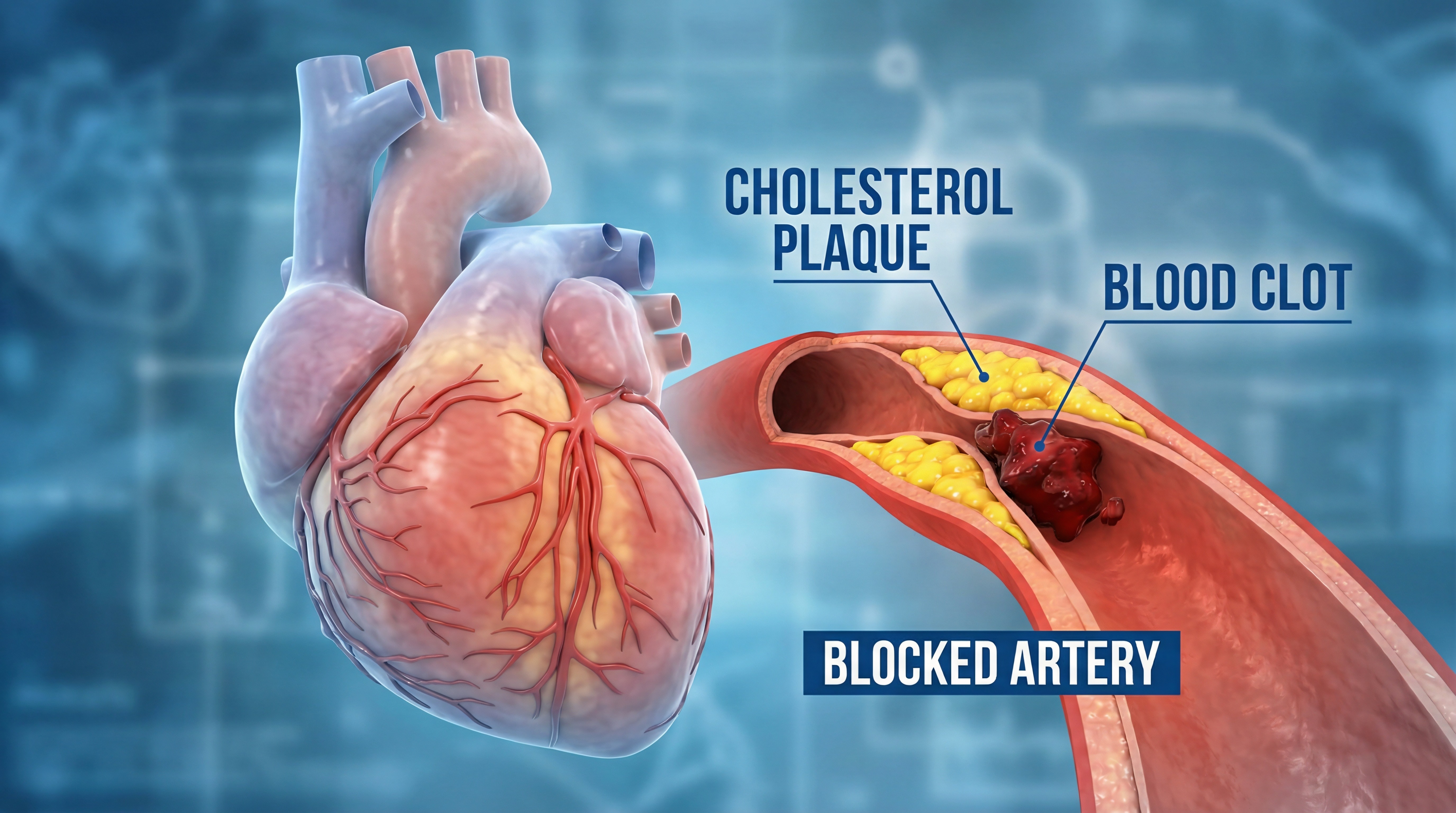
Plaque can build up inside your arteries for years before you feel any symptoms. By the time chest pain or shortness of breath appears, heart disease may already be advanced.
A coronary artery calcium (CAC) score is one way clinicians look for early signs of plaque in the arteries that supply blood to your heart. It helps estimate your risk of heart disease and can guide decisions about prevention.
What Is Plaque and Why Does It Matter?
Plaque is a mixture of fat, cholesterol, immune cells, and other substances that collect inside artery walls. As plaque builds up, it can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition that narrows and stiffens the arteries.
Plaque formation involves several changes inside the artery:
Immune cells absorb cholesterol and become trapped in the artery wall
Inflammation continues inside the vessel
A fibrous, hardened layer may form over softer plaque underneath
Arteries can stretch outward as plaque builds up. This process, called positive remodeling, helps preserve blood flow for years. Because of this, many people have no symptoms until plaque becomes more advanced.
Risk Factors for Plaque Buildup
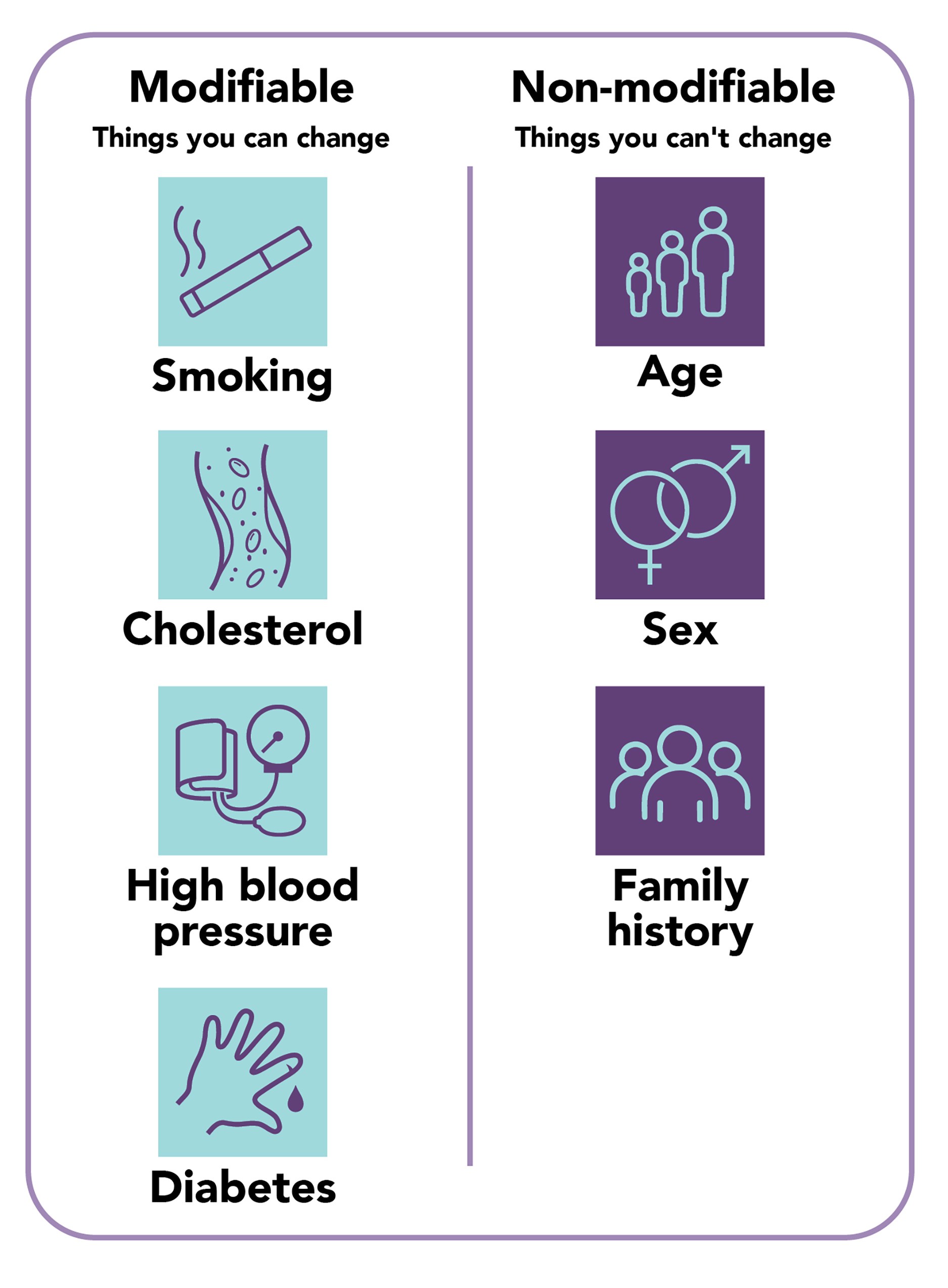
Some risk factors for heart disease can be changed. Others cannot.
Modifiable Risk Factors (Things You Can Change)
Smoking
High cholesterol
High blood pressure
Diabetes
These conditions directly affect artery health and contribute to plaque formation.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors (Things You Can’t Change)
Age
Sex
Family history
Even though you can’t change these, they still help clinicians estimate your overall cardiovascular risk.
What Is a Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) Score?
A coronary artery calcium score measures the amount of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries.
The test is done with a specialized CT scan called a CAC scan or calcium score test.
Here’s what to expect:
It’s quick and painless
No contrast dye or injections are needed
The scan usually takes just a few minutes
You can return to normal activities right away
The scan detects calcium deposits in artery walls. Calcium is a sign that plaque has been present for some time.
What Do Calcium Scores Mean?
Score of 0: No calcified plaque detected
Higher score: More calcified plaque and higher risk of heart disease
In general, the higher the score, the greater the risk of a heart attack or other atherosclerotic cardiovascular event.
What a Calcium Score Can Tell You
A calcium score can:
Estimate your risk of heart attack or stroke
Help clarify heart disease risk when it’s borderline or unclear
Guide conversations about prevention, including statin therapy
Support shared decision-making between you and your clinician
It’s most helpful for people whose risk is not clearly low or clearly high.
What a Calcium Score Cannot Tell You
A calcium score has important limits.
It does not:
Detect soft (non-calcified) plaque
Rule out coronary artery disease on its own
Show how narrow an artery is
Show whether a blockage is limiting blood flow
You can still have non-calcified plaque even if your calcium score is zero. If you have symptoms or high risk, your clinician may recommend additional testing.

Who Should Consider a Calcium Score?
A CAC scan is not recommended for everyone.
It may be discussed if you:
Are between ages 40–79
Have borderline or intermediate cardiovascular risk
Are unsure whether starting a statin makes sense
Have additional risk factors not fully captured in standard risk calculators
It is generally not used if you:
Already have known cardiovascular disease
Have had a prior heart attack, stent, or bypass surgery
Are already taking statins
Clearly need statin therapy regardless of the result
In those situations, the test would not change treatment decisions.
How a Calcium Score Fits Into Heart and Vascular Health
A coronary artery calcium score is one tool among many. It does not diagnose heart disease by itself, but it can provide valuable insight into plaque burden and long-term cardiovascular risk.
When combined with other information, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, diabetes, smoking history, age, and family history, it helps create a clearer picture of your vascular health.
If you’re unsure about your heart disease risk, it may be worth asking your clinician whether a calcium score could help guide your prevention plan.
References
American Heart Association. Coronary artery calcium test. Accessed February 5, 2026
Chen X, Zhao J, Cai Q, et al. Relationship between coronary artery calcium score and coronary stenosis. Cardiol Res Pract. 2023;2023:5538111. doi:10.1155/2023/5538111
Dawson LP, Lum M, Nerleker N, Nicholls SJ, Layland J. Coronary atherosclerotic plaque regression: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(1):66-82. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.10.035
Pahwa R, Jialal I. Atherosclerosis. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan.
Walter KL. What is a cardiac CT calcium score?JAMA. 2025;334(5):462. doi:10.1001/jama.2025.7567
Keep a Pulse on Progress
Explore our community and collaborate to build and utilize top-tier, trustworthy, and balanced medical education
