Last updated on
Who Should I See After Being Diagnosed with a Blood Clot?
KEY TAKEWAYS
- After a blood clot, you may need to see different clinicians who specialize in a certain type of medicine.
- Your primary care provider, or PCP, and care team can help coordinate your visits with specialists.
- Ask your PCP if you have any questions about which doctor you should see for your specific health needs.

When you’ve had a major event like a blood clot, the medical system can sometimes feel overwhelming. What type of doctor should you see? How can you find the specialists that you need?
WHAT IS AN EMERGENCY CARE SPECIALIST?
If you’re experiencing chest pain, difficulty breathing, a rapid heartbeat, lightheadedness or sudden weakness, numbness, or difficulty speaking, you should always go to the emergency room (ER) as soon as possible.
The doctors that treat you in the ER are called emergency care specialists. Treating clots early is critical to prevent serious complications.
After your visit, make an appointment to see your primary care provider, or PCP, a few days later. Your primary care team will help coordinate your care.
WHAT IS A PRIMARY CARE PROVIDER?
Your PCP is the doctor that you see for annual wellness visits and other routine care. Your primary care team may include doctors, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, medical assistants, and office staff. They play a few different roles, one of which is to coordinate your care when you have a complex medical situation. Your PCP is like the “quarterback” of your care team.
Your PCP will determine which specialists you should see. They’ll also provide referrals if necessary and keep an eye on reports from different specialists.
WHICH SPECIALISTS TREAT BLOOD CLOTS?
After a blood clot, your medical care may involve one or more specialists, or doctors who treat certain types of conditions. The specialist you’ll need depends on the specifics of your medical situation.
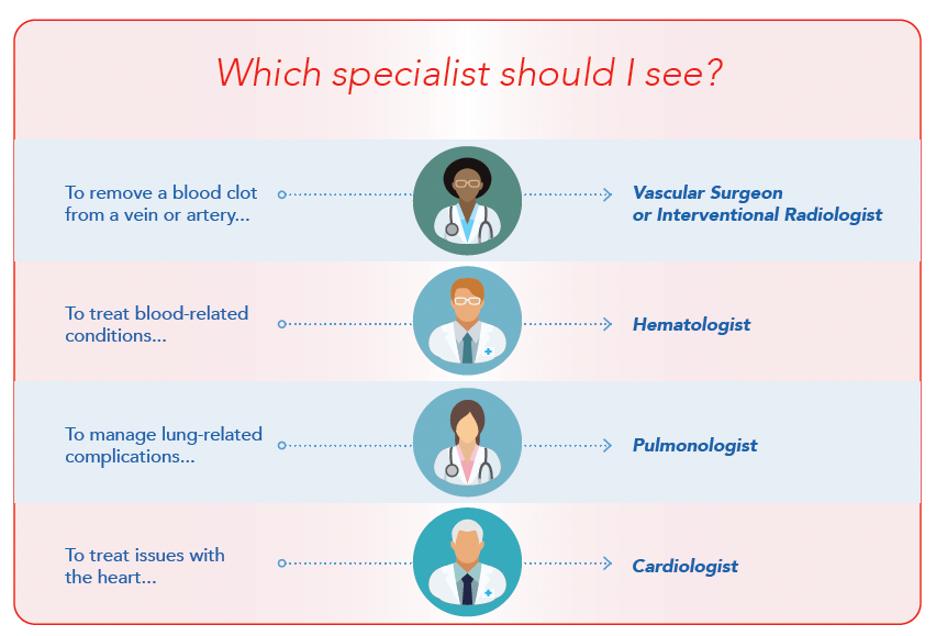
Interventional radiologist/vascular surgeon
- Interventional radiologists (IRs) use imaging, such as x-rays or CT scans, to perform certain medical procedures.
- If you need a surgery or procedure to remove a blood clot from a vein or artery, a vascular surgeon will open the affected blood vessel, remove the clot, and then repair the vessel.
Hematologist
- Hematologists specialize in treating diseases of the blood. A hematologist will often order tests to determine what’s causing your clots. They can also help you choose the right treatment to lower your risk of having another clot.
- If you take a blood thinner, you may be asked to follow up with your hematologist regularly. Your PCP might also be responsible for managing your blood thinners.
Pulmonologist
- A pulmonologist specializes in diseases of the lungs and other parts of the respiratory system. If you’ve experienced a pulmonary embolism (PE) and develop lung-related complications, you may be referred to a pulmonologist.
Cardiologist
- A cardiologist specializes in treating diseases of the heart and other parts of the cardiovascular system.
- You may need to see a cardiologist if a clot formed in a coronary artery (meaning that you had a heart attack), or if a blood clot in your lungs damaged your heart.
WHICH OTHER SPECIALISTS MIGHT I NEED TO SEE?
If your blood clot is thought to be caused or worsened by an underlying condition, you may need to see a different specialist entirely. For example, an endocrinologist specializes in treating hormonal conditions. If you have an autoimmune condition (in which your immune system is attacking your own tissues), you may need to see a rheumatologist. A vascular medicine specialist, who treats diseases that affect the blood vessels, could also be part of your care team.
HOW DO I FIND A NEW SPECIALIST?
In most cases, the best approach is to ask your PCP for a referral.
If you’re ever searching for a specialist on your own, it’s best to look for a doctor who’s board certified in that specialty. You can search for a doctor’s name and verify that they have board certification on the American Board of Medical Specialties website.
THE BOTTOM LINE
Ask your PCP or your care team for referrals to specialists that you’ll need. Talk with them about why they’re recommending certain specialists for you, and don’t be afraid to ask for more information. Contact your PCP if you have any questions about your care plan.
*Original version published in The Beat — February 2023. Read the full newsletter here.
REFERENCES
What Is a Primary Care Provider? – Cleveland Clinic
Interventional Radiology – Johns Hopkins Medicine
What is a Vascular Surgeon? – Society for Vascular Surgery
Hematology – Johns Hopkins Medicine
Pulmonologist – Cleveland Clinic
Cardiologist – Cleveland Clinic
Vascular Doctor – Cleveland Clinic